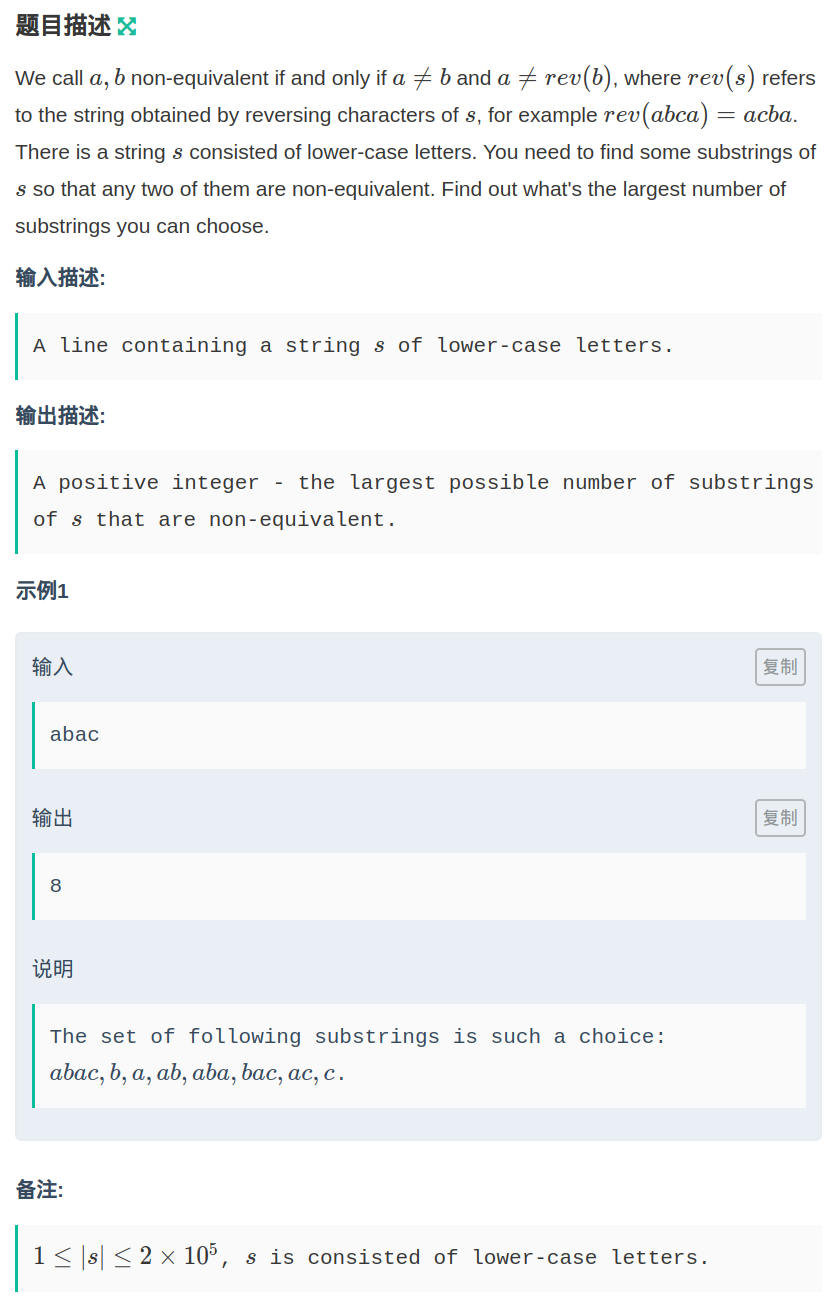
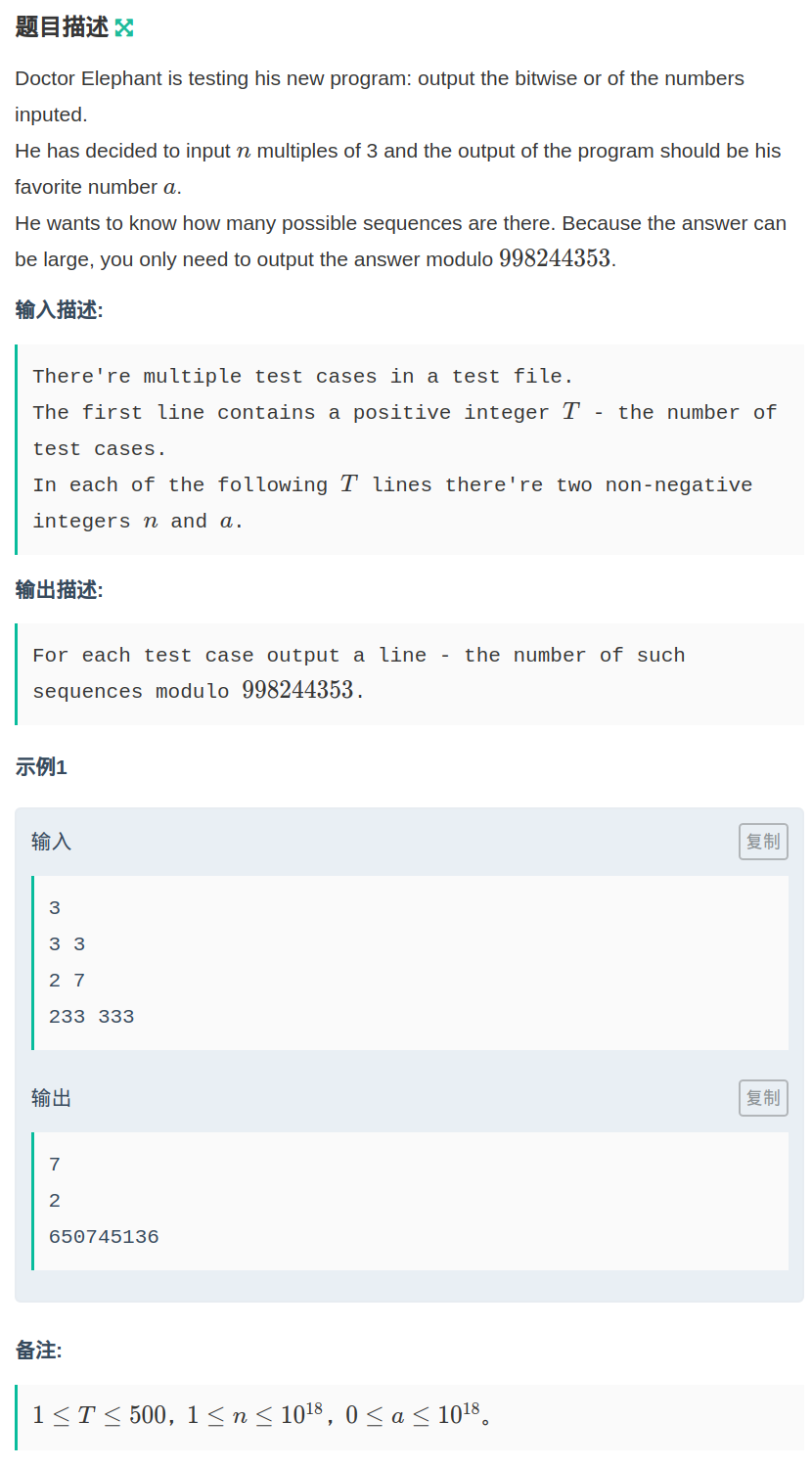
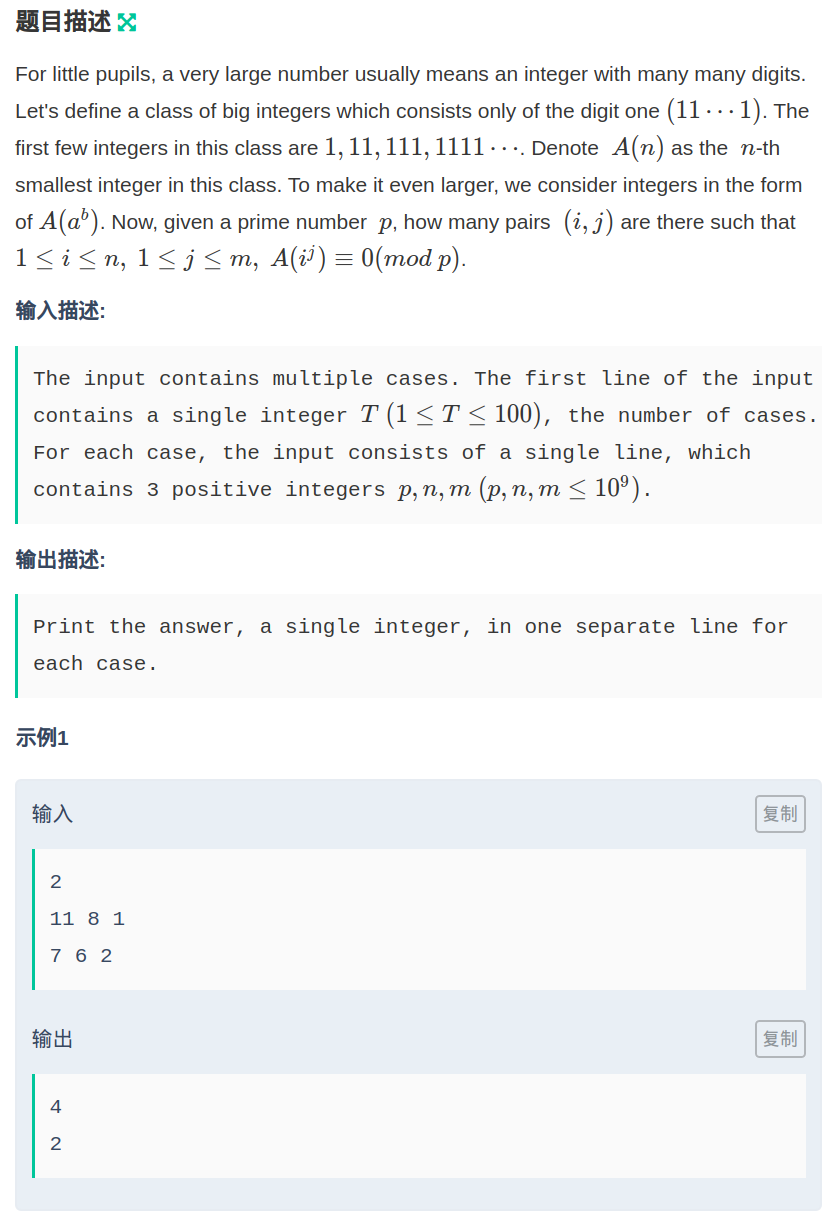
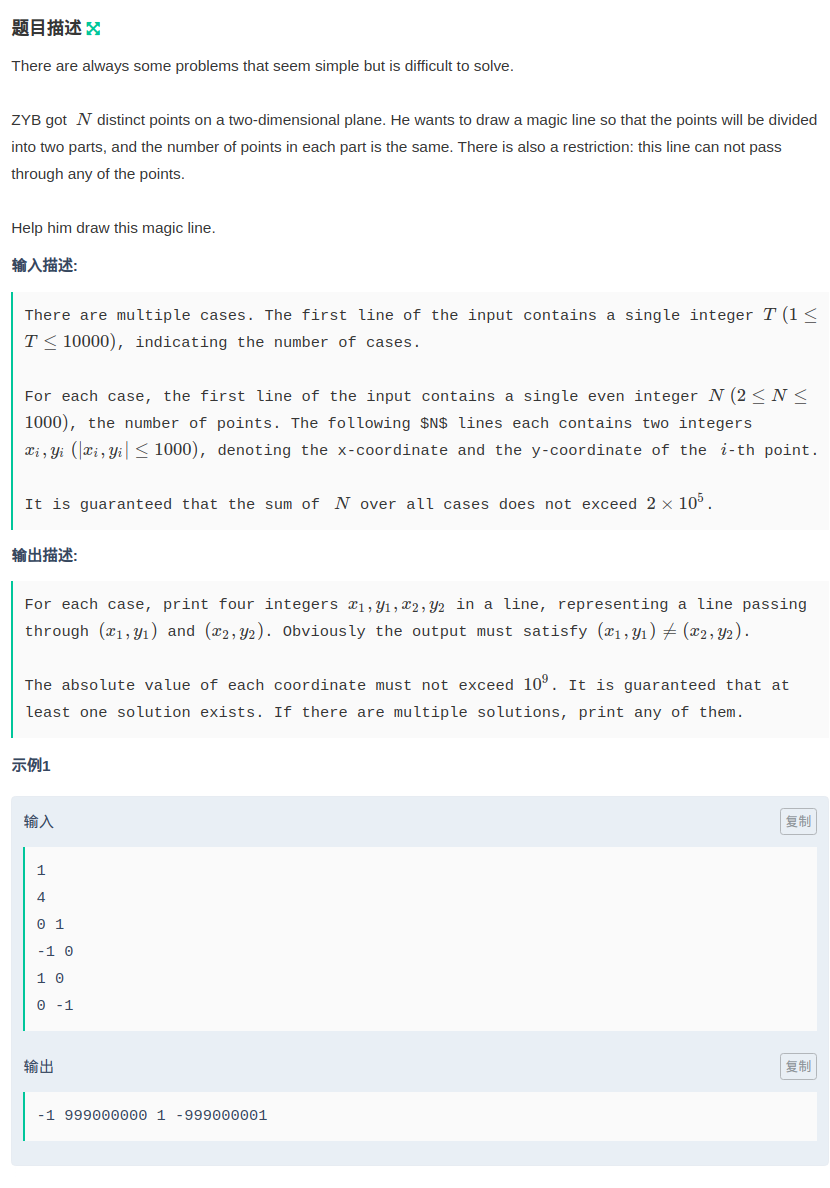
题目链接
Problem Description
There is an integer sequence a of length n and there are two kinds of operations:
0 l r: select some numbers from al…ar so that their xor sum is maximum, and print the maximum value.
1 x: append x to the end of the sequence and let n=n+1.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of input contains an integer T(T≤10), indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case:
The first line contains two integers n,m$(1≤n≤5×10^5,1≤m≤5×10^5)$, the number of integers initially in the sequence and the number of operations.
The second line contains n integers $a1,a2,…,an(0≤ai<2^{30})$, denoting the initial sequence.
Each of the next m lines contains one of the operations given above.
It’s guaranteed that $∑n≤10^6,∑m≤10^6,0≤x<2^{30}$.
And operations will be encrypted. You need to decode the operations as follows, where lastans denotes the answer to the last type 0 operation and is initially zero:
For every type 0 operation, let l=(l xor lastans)mod n + 1, r=(r xor lastans)mod n + 1, and then swap(l, r) if l>r.
For every type 1 operation, let x=x xor lastans.
Output
For each type 0 operation, please output the maximum xor sum in a single line.
Sample Input
1
3 3
0 1 2
0 1 1
1 3
0 3 4
Sample Output
1
3
题意
给一个长度为n的数组m个操作
- 0 x y 查询区间$[x,y]$取任意个数能异或出的最大值
- 1 x 向数组尾部添加一个数x
强制在线
题解
朴素的线性基只能查询1-n能异或出的最大值,这题我们可以保存$[1,n]$每个前缀线性基的状态,查询x,y时只需要查询第y个前缀的线性基就行
但是前缀里会有1-x的线性基影响结果,我们可以在插入线性基时做处理,如果在第pos位上已经有数,且这个数的插入时间比我当前数的插入时间早,那么就把当前要插入的数与该数交换,当前插入时间也交换,直至当前数无法插入或变为0
这样可以让前缀线性基里的数都是越新的,查询的时候判断线性基上数的插入时间是否大于等于x,如果大于x就可以使用这个数。这样处理的正确性是因为线性基插入不受顺序影响,同一组数以不同顺序插入,最后得到的线性基都是等价的
代码
1 |
|