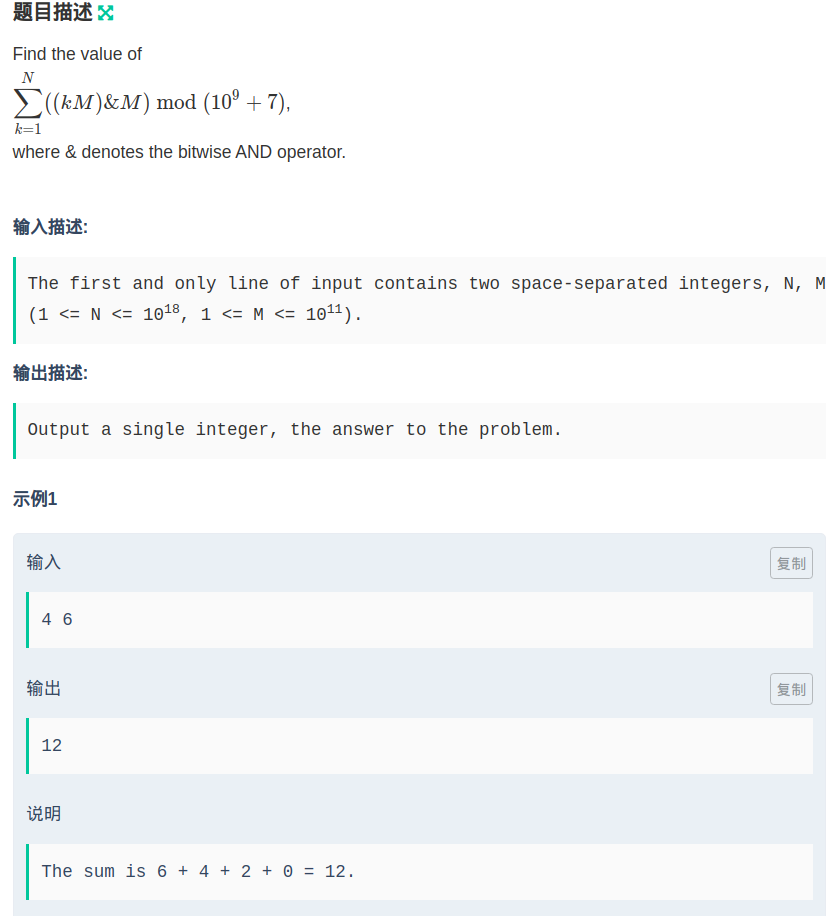
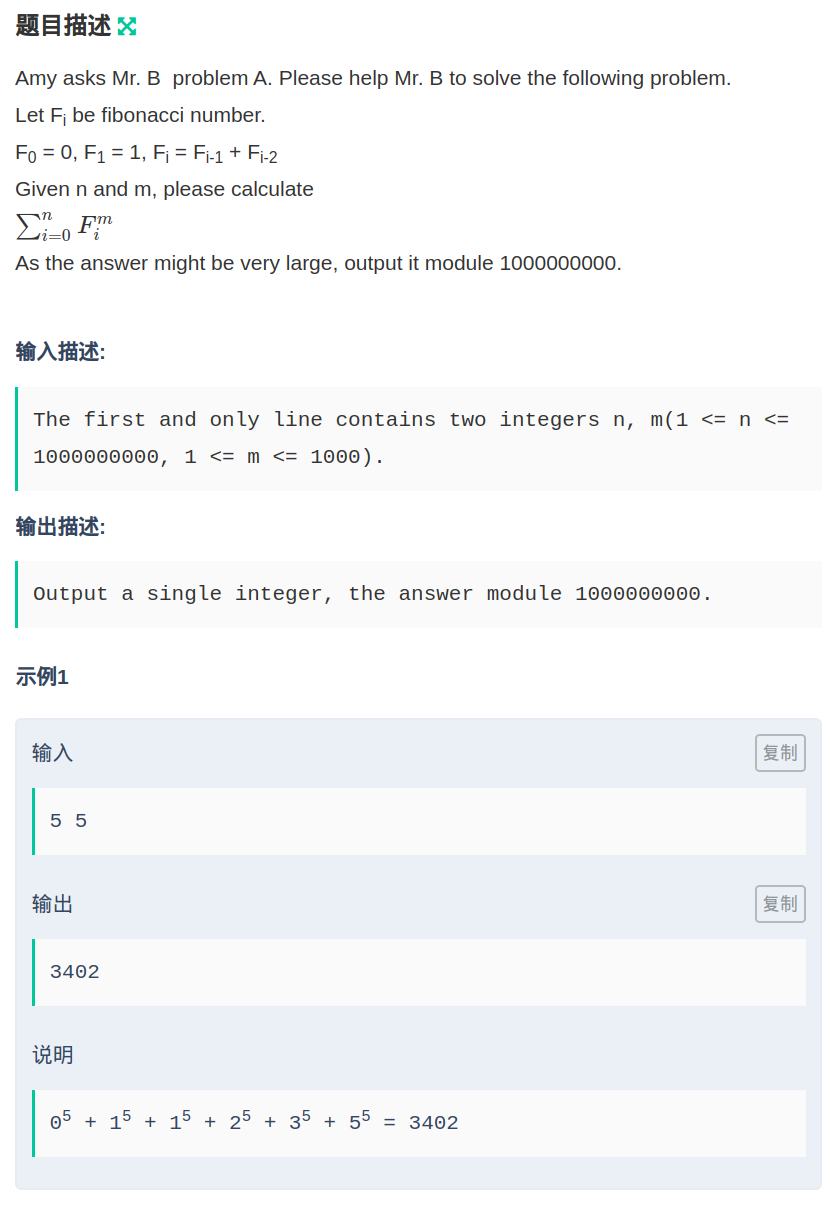
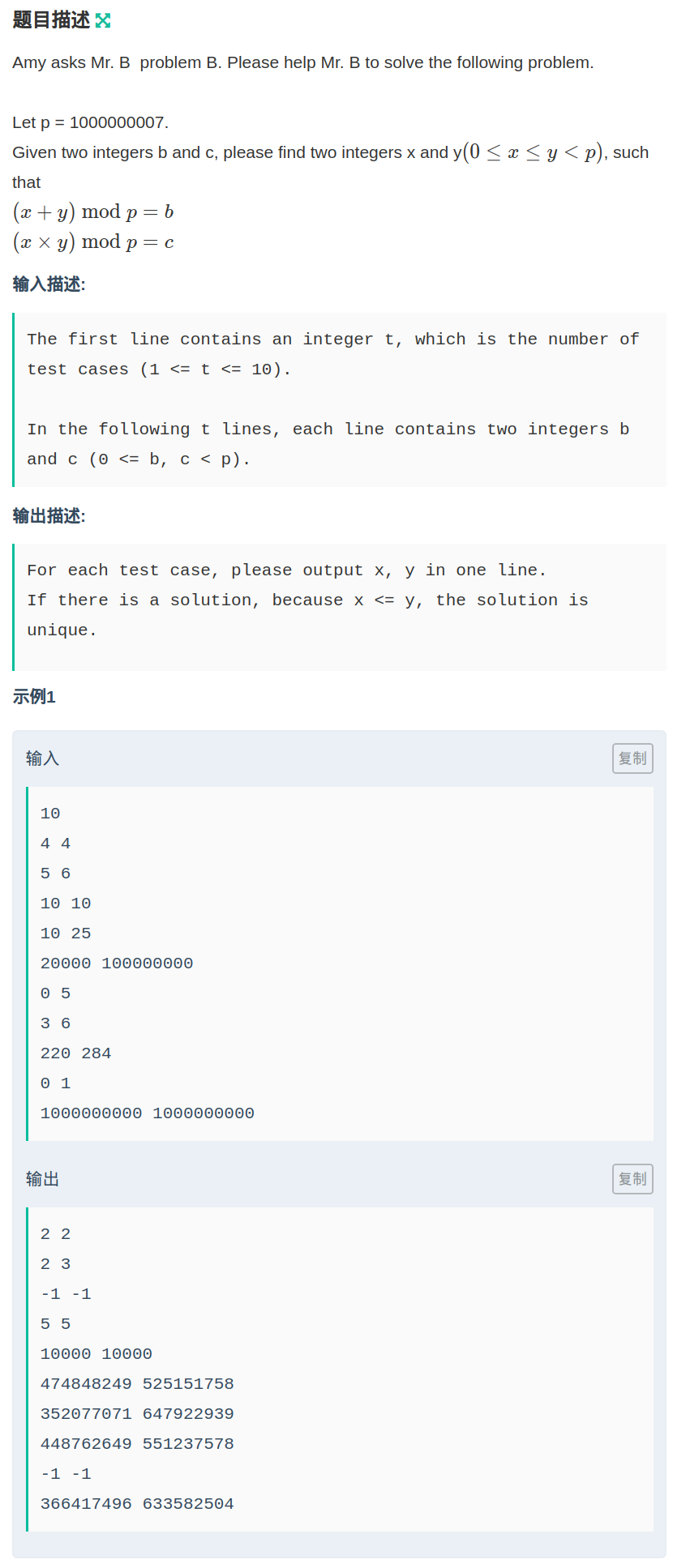
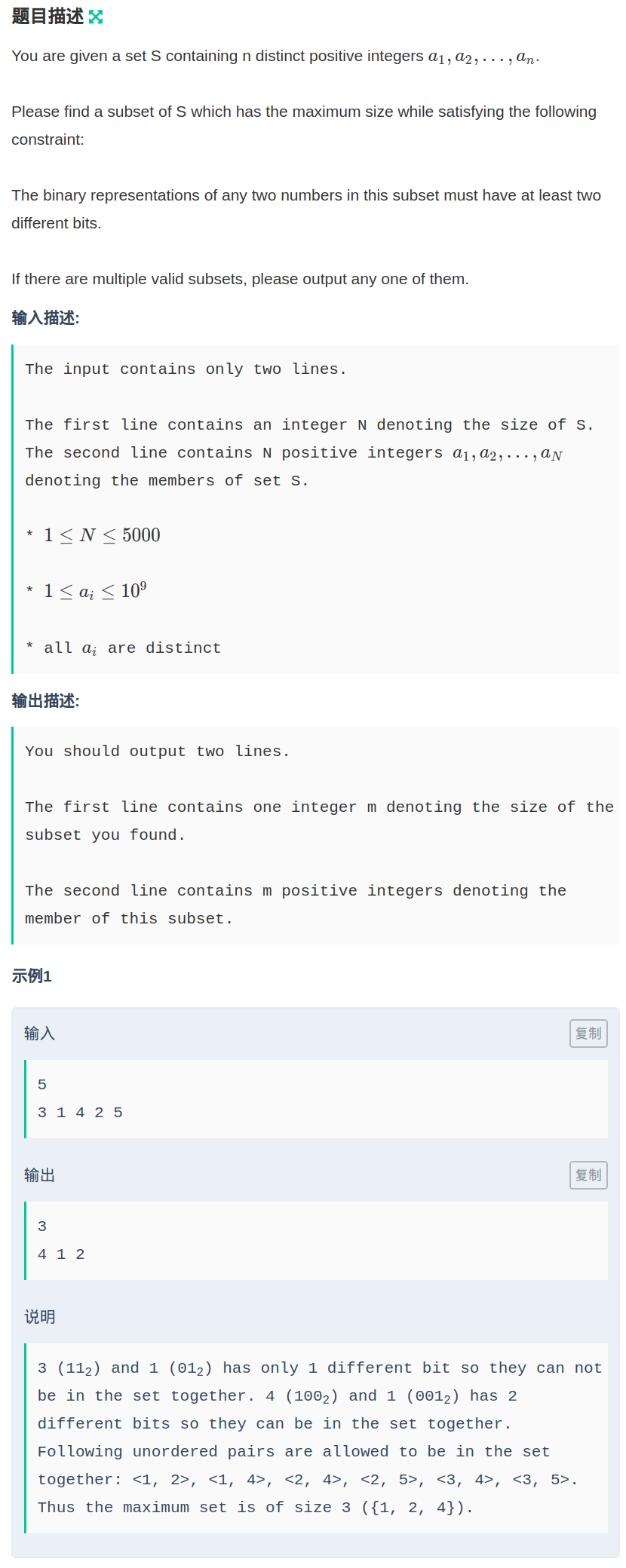
题目链接
Problem Description
Rikka’s birthday is on June 12th. The story of this problem happens on that day.
Today is Rikka’s birthday. Yuta prepares a big cake for her: the shape of this cake is a rectangular of n centimeters times m centimeters. With the guidance of a grimoire, Rikka is going to cut the cake.
For simplicity, Rikka firstly builds a Cartesian coordinate system on the cake: the coordinate of the left bottom corner is (0,0) while that of the right top corner is (n,m). There are K instructions on the grimoire: The ith cut is a ray starting from (xi,yi) while the direction is Di. There are four possible directions: L, passes (xi−1,yi); R, passes (xi+1,yi); U, passes (xi,yi+1); D, passes (xi,yi−1).
Take advantage of the infinite power of Tyrant’s Eye, Rikka finishes all the instructions quickly. Now she wants to count the number of pieces of the cake. However, since a huge number of cuts have been done, the number of pieces can be very large. Therefore, Rikka wants you to finish this task.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer T(1≤T≤100), the number of the test cases.
For each test case, the first line contains three positive integers n,m,K(1≤n,m≤109,1≤K≤105), which represents the shape of the cake and the number of instructions on the grimoire.
Then K lines follow, the ith line contains two integers xi,yi(1≤xi<n,1≤yi<m) and a char Di∈{‘L’,’R’,’U’,’D’}, which describes the ith cut.
The input guarantees that there are no more than 5 test cases with K>1000, and no two cuts share the same x coordinate or y coordinate, i.e., ∀1≤i<j≤K, xi≠xj and yi≠yj.
Output
For each test case, output a single line with a single integer, the number of pieces of the cake.
Hint
The left image and the right image show the results of the first and the second test case in the sample input respectively. Clearly, the answer to the first test case is 3while the second one is 5.
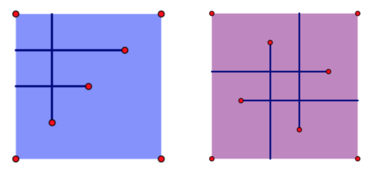
Sample Input
2
4 4 3
1 1 U
2 2 L
3 3 L
5 5 4
1 2 R
3 1 U
4 3 L
2 4 D
Sample Output
3
5
题意
矩形平面上有一些水平或垂直的射线,问这些射线把这个矩形分成了几块
题解
有一个神仙公式叫欧拉公式:$V-E+F=2$,V是点数,E是边数,F是平面数
V = 矩形四个点 + 射线端点n + 射线到矩形交点n + 射线间焦点c = 2n + 4 + c
E = 矩形四条边 + 矩形四条边被射线分割的边n + 射线n条 + 射线与射线分割的边(每个交点都会产生2条新边) 2c
所以F = 2 + c,再扣掉矩形外的平面答案就是1 + c
求交点个数只要从左往右遍历垂直射线,遍历过程中每遇到水平射线左端点则在树状数组上+1,遇到水平射线又端点就在树状数组上-1
代码
1 |
|